
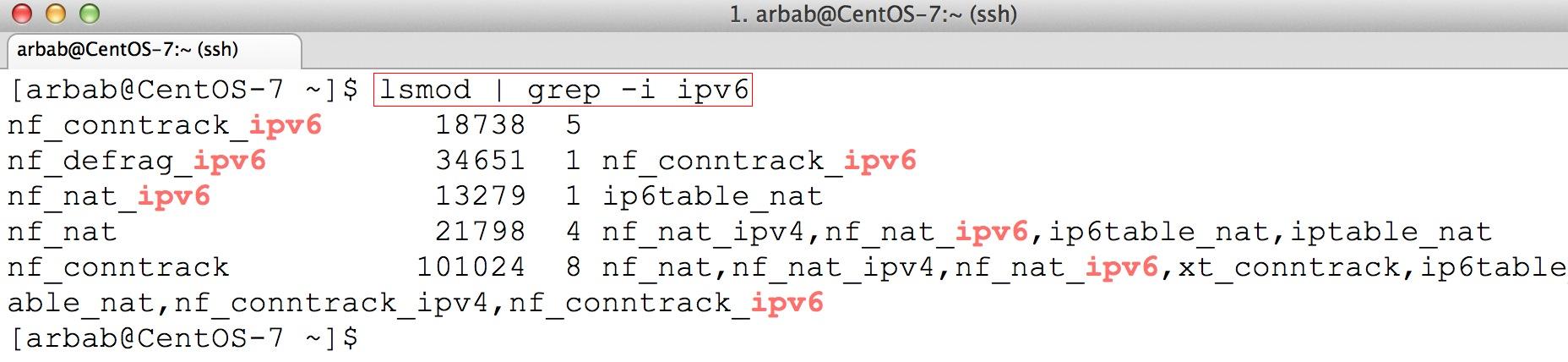
Here are details on how to disable IPv6 on Redhat / CentOS 6 / CentOS 7: 1. Update /etc/sysctl.conf: 2. Update config file in/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 and /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens160: 3. Edit /etc/sysconfig/network file and add 'no' to NETWORKINGIPV6.
This step by step by guide to configure IPv6 address is validated on RHEL and CentOS 7.IPv6 can act as a replacement for the IPv4 network protocol. The major problem it solves is the exhaustion of IPv4 addresses by using a much larger network address space. It also provides a number of enhancements and new features for network configuration management and support for future protocol changes.The key reason IPv6 is not yet in wide deployment is that the core protocol does not have a simple way for systems that only have IPv6 addresses to communicate with systems that only have IPv4 addresses.An IPv6 address is a 128-bit number, normally expressed as eight colon-separated groups of four hexadecimal nibbles (half-bytes). Each nibble represents four bits of the IPv6 address, so each group represents 16 bits of the IPv6 address. 2001:0001:0001:1443:0000:0000:0000:0400To make it easier to write IPv6 addresses, leading zeros in a colon-separated group do not need to be written. However at least one nibble must be written in each field.
Zeros which follow a non zero nibble in the group do not need to be written. 2001:1:1:1443:0:0:0:400Since addresses with long strings of zeros are common, combine one or more groups of consecutive zeros with exactly one:: block. 2001:1:1:1443::400Notice that under these rules 2001:1:1:1443::400 would be another less convenient way to write the example address. But it is a valid representation of the same address, and this can confuse administrators new to IPv6.Some tips for writing consistently readable addresses. Always suppress all the leading zeros in a group.
Use:: to shorten as much as possible. If two runs of zeros are equal in length, shorten the leftmost run of zeros by preference. Although it is allowed, do not use:: to shorten one group of zeros, Use:0: instead, and save:: for runs of zeros longer than a single group. Always use lowercase letters for hexadecimal numbers a through f. Comparison of nm-setting and ifcfg-. directivesThe following table maps some of the key NetworkManager settings name relevant to IPv6 connections to ifcfg-.
directives. Nmcli con modifcfg-.
fileEffectipv6.method manualIPV6AUTOCONF=noIPv6 is configured staticallyipv6.method autoIPV6AUTOCONF=yesWill configure network settings using SLAAC from router advertisements.ipv6.method dhcpIPV6AUTOCONF=noDHCPV6C=yesWill configure network settings by using DHCPv6, but not SLAACipv6. Next look out for your Ethernet card on which you wish to configure IPv6 address. If your NIC card does not appear on the list then you can add a new device.

Centos 7 Disable Ipv6 Firewall
Since for me my device ( eno50) exists, so I will select the device and select EditThis will bring you the main configuration page where you must give all the details to configure IPv6 address. Since I do not want to add IPv4 address to the same Ethernet device, I have disabled the IPv4 option.Provide the IPv6 address/subnet and the gateway.

Make sure you select Automatically ConnectLastly click OK to exit the utility.Now let us check the network configuration of eno50. # nmcli con add con-name eno49 type ethernet ifname eno49 ip6 2001:1:1:1443::433/122 gw6 2001:1:1:1443::43FConnection 'eno49' (e6f51cfa-4dba-4fbb-b7fa-9c777a6edb52) successfully added. I wanted to compose you this little bit of word in order to say thank you yet again over the fantastic techniques you’ve featured on this site. It was quite extremely generous with you to allow unhampered all that a number of people could possibly have marketed for an e-book to end up making some bucks for their own end, chiefly given that you could possibly have done it in the event you desired. The ideas likewise acted as the fantastic way to be aware that most people have a similar dreams just as my personal own to see more when considering this problem. I know there are lots of more fun moments in the future for individuals who scan your blog.
Disable IPv6 on Centos 7 / RHEL 7. Why i am telling to disable IPv6 because still IPv6 is not in production use. If you enable it in production servers who knows how it impact vulnerability to hack into our system / servers. To avoid un-necessary headache simple keep in disabled mode until we use.IPv6(Internet Protocol version 6) is the internet’s next-generation protocol and it is the most latest version of the internet protocol. IPv6 allows more users and devices to communicate on the Internet by using bigger numbers to create IP addresses.
